PID Compensation Animated
The PID controller has the standard form Kp+Ki/s+Kds. Therefore, the closed loop transfer function of the whole system becomes
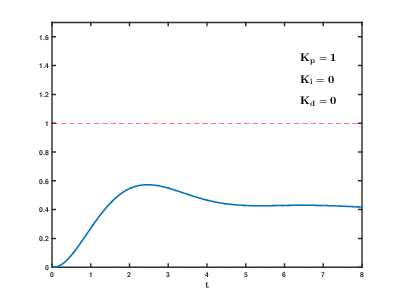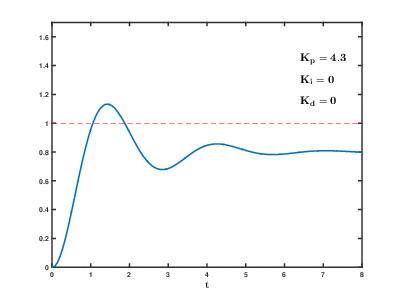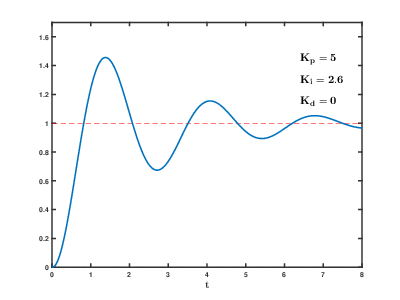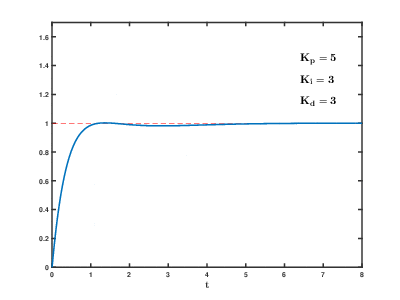
As the proportional, integral and derivative terms of the PID compensator are increased, the evolution of the step response, from the initial uncompensated response (corresponding to PID coefficents Kp=1, Ki=0, Kd=0) to the final desired response is depicted. The following effects of PID compensation can be readily observed:
- The proportional term increases the speed of the system. It also decreases the residual steady state error of the step response, but can not eliminate it completely.
- The integral term eliminates the residual steady state error of the step response, but adds undesired "oscillations" to the transient response (overshoot).
- The derivative term "damps out" the undesired oscillations in the transient response.
Relevante Bilder












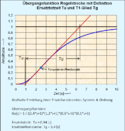

























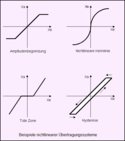



Relevante Artikel
RegelungstechnikRegelungstechnik ist eine Ingenieurwissenschaft, welche diejenigen Regelungsvorgänge behandelt, die in der Technik vorkommen. .. weiterlesen