Crisis salina del Messiniense
Obra derivada de / Lavoro derivato / Derivative work:
A possible cause of the subsequent closure of the connection with the Atlantic is the removal of plaque collapsing (slab rollback) during a phenomenon of subduction. (0:13 minute) in combination to the change of sea level (minute 0:28).
Following the complete closure between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea (0:31 minutes) the level of the Mediterranean Sea dropped rapidly just because there was no supply of water coming from the Atlantic. The rivers that flowed into the sea, began to run the seabed creating deep ruts and waterfalls in its delta. The evaporation (0:35 minutes) produced the storage of large amounts of salt on the sea bottom (0:39 minutes).
Presumably, during the period in which the level of the Mediterranean Sea was 1500-1200 meters lower than today, some mammals passed through Africa and Europe, through the present Gibraltar Strait. (minute 0:44).
It is believe that the crisis saline, ended with a flood of enormous dimensions of the Atlantic in the Mediterranean Sea 5.33 million years ago, through an passage opened in the current Straits of Gibraltar (minute 0:52). When the strait collapsed to the level of the sea, the Atlantic overflowed in the Mediterranean Sea and the water, the erosion due to the waters dug a groove getting bigger, finishing the filling process catastrophic, that lasted only few months. (minute 1:10).
Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
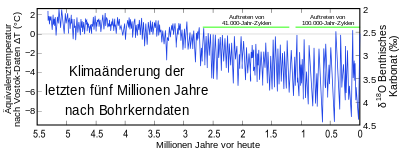
Känozoisches EiszeitalterDas Känozoische Eiszeitalter ist das gegenwärtige Eiszeitalter, das Eiszeitalter des Känozoikums (Erdneuzeit) in Abgrenzung zu den Eiszeitaltern des Paläozoikums und des Präkambriums. Sein Beginn korrespondiert mit der allmählichen Vergletscherung der Antarktis vor rund 34 Millionen Jahren. Vor etwa 2,7 Millionen Jahren setzte auch die verstärkte Eisbildung in der Arktis ein. Ab dieser Zeit wechseln sich (längere) Kaltzeiten (Glaziale) mit (kürzeren) Warmzeiten (Interglaziale) ab. .. weiterlesen
NeogenDas Neogen ist ein Abschnitt der Erdgeschichte. Nach heutiger Definition wird das Erdzeitalter des Känozoikums geochronologisch in drei Abschnitte eingeteilt: in das Paläogen, das Neogen und das Quartär. In der Chronostratigraphie ist das Neogen damit das zweithöchste System. Es entspricht dem veralteten Begriff Oberes Tertiär oder Jungtertiär.Erdzeitalter: Känozoikum System: Quartär (2,588–0 mya) System: Neogen (23,03–2,588 mya) System: Paläogen (66–23,03 mya) .. weiterlesen