Deltaretrovirus
| Deltaretrovirus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
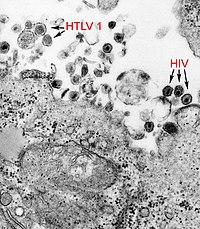 Beispiel: HTLV-1 im EM. | ||||||
| Systematik | ||||||
| Taxonomische Merkmale | ||||||
| ||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||
| Deltaretrovirus | ||||||
| Links | ||||||
|
Die Deltaretroviren sind eine Gattung innerhalb der Familie der Retroviren. Zu ihnen gehören beispielsweise das Bovine Leukämie-Virus sowie die Primaten-Viren wie die humanpathogenen HTLV-1 und HTLV-2. Nahe Verwandte von HTLV-1 und -2 sind die simianen (Affen)-Viren, STLV-1 und STLV-2. Die Deltaretroviren werden von Tier zu Tier weitergegeben und verursachen T- oder B-Zell-Leukämien. Von den Deltaretroviren sind keine endogenen Retrovirus-Varianten bekannt.
Den Deltaretroviren wurden 1998 aufgrund phylogenetischer Verwandtschaft der Rang einer Gattung zugeordnet. Sie besitzen die akzessorischen Gene tax und rex, die einander überlappen.
Systematik
Die Gattung (Genus) Deltavirus besteht gemäß ICTV mit Stand November 2018 aus den folgenden Arten (Spezies) bzw. Unterarten (Subspezies),[2] die Virusnamen sind dem 9. Report des ICTV (2011) entnommen:[3]
- Genus Deltaretrovirus
- Spezies Bovines Leukämie-Virus (en. Bovine leukemia virus, BLV)
- Spezies Primaten-T-lymphotrophes Virus 1 (en. Primate T-lymphotropic virus 1)
- Humanes T-lymphotropes Virus 1 (englisch Human T-lymphotropic virus 1, Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus, HTLV-1, Erstbeschreibung 1979/1980)[4]
- Simianes T-lymphotropes Virus 1 (englisch Simian T-lymphotropic virus 1, STLV-1)
- Spezies Primaten-T-lymphotrophes Virus 2 (en. Primate T-lymphotropic virus 2)
- Humanes T-lymphotropes Virus 2 (HTLV-2, Erstbeschreibung 1982)[5]
- Simianes T-lymphotropes Virus 2 (STLV-2)
- Spezies Primaten-T-lymphotrophes Virus 3 (en. Primate T-lymphotropic virus 3)[6]
- Humanes T-lymphotropes Virus 3 (HTLV-3, Erstbeschreibung 2005)
- Simianes T-lymphotropes Virus 3 (STLV-3)
- Bis dato keiner Spezies zugeordnete Viren:
- Humanes T-lymphotropes Virus 4 (HTLV-4, Erstbeschreibung 2005, identisch mit Simianem T-lymphotropen Virus 4, STLV-4)
- Simianes T-lymphotropes Virus 5 (STLV-5, Erstbeschreibung 2009)
Anmerkungen:
- HTLV-3, HTLV-III, sowie LAV oder ARV sind frühere Bezeichnungen von HIV-1 (Gattung Lentivirus, Krankheit AIDS) seit der Erstbeschreibung 1983 bis zur Festlegung der neuen Bezeichnung durch das ICTV 1986. Seit 2005 bezeichnet HTLV-3 ein Virus der Spezies Primate T-lymphotropic virus 3 der hier betrachteten Gattung Deltaretrovirus.
- HTLV-4, HTLV-IV, sowie LAV-2 sind Bezeichnungen, die kurzzeitig für das 1986 entdeckte HIV-2 (ebenfalls Gattung Lentivirus, Krankheit AIDS) gebräuchlich waren.[7] Seit 2005 bezeichnet HTLV-4 ebenfalls ein (bis 2018 noch keiner Spezies zugewiesenes) Virus der hier betrachteten Gattung Deltaretrovirus.
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Commelina yellow mottle virus, EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL #35)
- ↑ ICTV: Master Species List 2018a v1 (Memento des vom 14. März 2019 im Internet Archive) Info: Der Archivlink wurde automatisch eingesetzt und noch nicht geprüft. Bitte prüfe Original- und Archivlink gemäß Anleitung und entferne dann diesen Hinweis. MSL including all taxa updates since the 2017 release. Fall 2018 (MSL #33)
- ↑ Reverse Transcribing DNA and RNA Viruses: Retroviridae (Memento des vom 15. August 2020 im Internet Archive) Info: Der Archivlink wurde automatisch eingesetzt und noch nicht geprüft. Bitte prüfe Original- und Archivlink gemäß Anleitung und entferne dann diesen Hinweis., 9. Report des ICTV (2011)
- ↑ B. J. Poiesz, F. W. Ruscetti, A. F. Gazdar, P. A. Bunn, J. D. Minna, R. C. Gallo: Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980; 77, S. 7415–7419. PMID 6261256.
- ↑ V. S. Kalyanaraman, M. G. Sarngadharan, M. Robert-Guroff, I. Miyoshi, D. Golde, R. C. Gallo: A new subtype of human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-II) associated with a T-cell variant of hairy cell leukemia. In: Science. 1982;218, S. 571–573. PMID 6981847.
- ↑ SIB: Primate T-lymphotropic virus 3, auf: ViralZone
- ↑ [1] at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
This image revealed the presence of both the human T-cell leukemia type-1 virus (HTLV-1), (also known as the human T lymphotropic virus type-1 virus), and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1), a human oncoretrovirus, is the etiologic agent of adult T-cell leukemia, and of tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-1–associated myelopathy. Two closely related retroviruses, HIV-1 and HIV-2, have been identified as causing AIDS in different geographic regions. HIV-1 causes most cases of AIDS in the U.S., with only a few cases of HIV-2 having been found in the U.S. Epidemiologically, HIV-2 has been found to be mostly an infection of persons from West Africa.
