Apoptotic Protease-activating Factor 1
| Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Apaf-1 | ||
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 1.248 Aminosäuren, 141.840 Da | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
| Orthologe (Mensch) | ||
| Entrez | 317 | |
| Ensembl | ENSG00000120868 | |
| UniProt | O14727 | |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_001160.2 | |
| Refseq (Protein) | NP_001151.1 | |
| PubMed-Suche | 317 | |
Apaf-1 ist ein Protein, welches eine Rolle bei der Einleitung des programmierten Zelltods (Apoptose) spielt.
Eigenschaften
Beim intrinsischen oder mitochondrialen Weg der Apoptose kommt es durch Stresssignale zur Inaktivierung des Proteins Bcl-2. Durch die Inaktivierung dieses anti-apoptotischen Faktors kommt es zur Apoptose.
Aktives Bcl-2 verhindert nämlich die Anlagerung eines Dimers der Proteine Bak und Bax an die Mitochondrienaußenmembran. Durch die Inaktivierung von Bcl-2 lagert sich das Bak-Bax-Dimer an die Mitochondrienaußenmembran an und es kommt zur Bildung einer Pore in der äußeren Mitochondrienmembran. Durch diese Porenbildung gelangt Cytochrom c aus dem Mitochondrium ins Zytosol. Diese Lokalisation des Cytochrom c im nichtursprünglichen Ort ist ein Apoptosesignal, denn das Cytochrom c bindet im Zytosol an Apaf-1. Durch die Bindung von Cytochrom c an Apaf-1 entsteht das Apoptosom („The wheel of death“). Das Apoptosom aktiviert die Initiator-Caspase Pro-Caspase 9, die dann autokatalytisch sich selbst spaltet und anschließend weitere Caspasen durch Spaltung aktiviert. Durch die Caspase-Kaskade wird der Abbau der Proteine eingeleitet.
Apaf-1 bindet an APIP,[1] BCL2-like 1[2][3] Caspase-9,[4][1][5][2][3] HSPA4,[6] und NLRP1.[4]
Apaf-1 wird in allen Zelltypen gebildet. Am meisten wird es in der erwachsenen Milz und in peripheren Leukozyten gebildet sowie im fötalen Gehirn, Niere und Lunge. Die Isoform 1 wird im Herzen gebildet. Isoform 6 aktiviert die Pro-Caspase 9 schwächer.
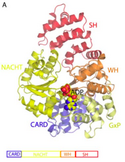
Strukturell enthält Apaf-1 eine CARD-Domäne mit einem greek key aus sechs Helices, eine Rossman-Faltung zur Bindung von Nukleotiden, gefolgt von einem kurzen helikalen Strukturmotiv und einer winged-helix-Proteindomäne.[7] Apaf-1 ist das Homolog von ced-4 aus Caenorhabditis elegans.[8]
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b Cho DH, Hong YM, Lee HJ, Woo HN, Pyo JO, Mak TW, Jung YK: Induced inhibition of ischemic/hypoxic injury by APIP, a novel Apaf-1-interacting protein. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279. Jahrgang, Nr. 38, September 2004, S. 39942–50, doi:10.1074/jbc.M405747200, PMID 15262985.
- ↑ a b Hu Y, Benedict MA, Wu D, Inohara N, Núñez G: Bcl-XL interacts with Apaf-1 and inhibits Apaf-1-dependent caspase-9 activation. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 95. Jahrgang, Nr. 8, April 1998, S. 4386–91, doi:10.1073/pnas.95.8.4386, PMID 9539746, PMC 22498 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ a b Pan G, O'Rourke K, Dixit VM: Caspase-9, Bcl-XL, and Apaf-1 form a ternary complex. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273. Jahrgang, Nr. 10, März 1998, S. 5841–5, doi:10.1074/jbc.273.10.5841, PMID 9488720.
- ↑ a b Chu ZL, Pio F, Xie Z, Welsh K, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Godzik A, Reed JC: A novel enhancer of the Apaf1 apoptosome involved in cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation and apoptosis. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276. Jahrgang, Nr. 12, März 2001, S. 9239–45, doi:10.1074/jbc.M006309200, PMID 11113115.
- ↑ Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X: Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. In: Cell. 91. Jahrgang, Nr. 4, November 1997, S. 479–89, doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80434-1, PMID 9390557.
- ↑ Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Balkir L, Robbins PD, Alnemri ES: Negative regulation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome by Hsp70. In: Nature Cell Biology. 2. Jahrgang, Nr. 8, August 2000, S. 476–83, doi:10.1038/35019510, PMID 10934467.
- ↑ Riedl SJ, Li W, Chao Y, Schwarzenbacher R, Shi Y: Structure of the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 bound to ADP. In: Nature. 434. Jahrgang, Nr. 7035, April 2005, S. 926–33, doi:10.1038/nature03465, PMID 15829969.
- ↑ H. Zou, W. J. Henzel, X. Liu, A. Lutschg, X. Wang: Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. In: Cell. Band 90, Nummer 3, August 1997, S. 405–413, PMID 9267021.
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
Autor/Urheber: Rjoo317, Lizenz: CC BY-SA 3.0
Structure of Apaf-1, an apoptosis-related protein with domains similar to NLR family proteins