Airy-Funktion
Die Airy-Funktion bezeichnet eine spezielle Funktion in der Mathematik. Die Funktion und die verwandte Funktion , die ebenfalls Airy-Funktion genannt wird, sind Lösungen der linearen Differentialgleichung
auch bekannt als Airy-Gleichung. Sie beschreibt unter anderem die Lösung der Schrödinger-Gleichung für einen linearen Potentialtopf.
Die Airy-Funktion ist nach dem britischen Astronomen George Biddell Airy benannt, der diese Funktion in seinen Arbeiten in der Optik verwendete (Airy 1838). Die Bezeichnung wurde von Harold Jeffreys eingeführt.
Definition
Für reelle Werte ist die Airy-Funktion als Parameterintegral definiert:
Eine zweite, linear unabhängige Lösung der Differentialgleichung ist die Airy-Funktion zweiter Art :
Eigenschaften
Asymptotisches Verhalten
Für gegen lassen sich und mit Hilfe der WKB-Näherung approximieren:
Für gegen gelten die Beziehungen:
Nullstellen
Die Airy-Funktionen haben nur Nullstellen auf der negativen reellen Achse.[1] Die ungefähre Lage folgt aus dem asymptotischen Verhalten für zu
Spezielle Werte
Die Airy-Funktionen und ihre Ableitungen haben für die folgenden Werte:
Hierbei bezeichnet die Gammafunktion. Es folgt, dass die Wronski-Determinante von und gleich ist.
Fourier-Transformierte
Direkt aus der Definition der Airy-Funktion (siehe oben) folgt deren Fourier-Transformierte.
Man beachte die hier verwendete symmetrische Variante der Fourier-Transformation.
Weitere Darstellungen
- Unter Verwendung der hypergeometrischen Funktion
- Für lassen sie sich auch mit der modifizierten Bessel-Funktion erster Art so darstellen:
- Eine andere unendliche Integraldarstellung für lautet
- Es gibt die Reihendarstellungen[2]
Komplexe Argumente
und sind ganze Funktionen. Sie lassen sich also auf der gesamten komplexen Ebene analytisch fortsetzen.
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
 |  | 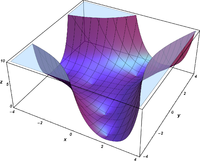 | 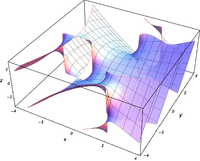 |
 |  |  |  |
Verallgemeinerungen
Definiere
wobei die hypergeometrische Funktion ist. Dann gibt es folgende Verallgemeinerungen des Airy-Integrals
Verwandte Funktionen
Airy-Zeta-Funktion
Zu der Airy-Funktion lässt sich analog zu den anderen Zeta-Funktionen die Airysche Zeta-Funktion definieren als[3]
wobei die Summe über die reellen (negativen) Nullstellen von geht.
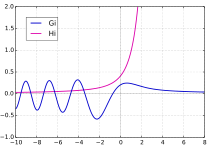
Scorersche Funktionen
Manchmal werden auch die beiden weiteren Funktionen und zu den Airy-Funktionen dazugerechnet. Die Integral-Definitionen lauten[4]
Sie lassen sich auch durch die Funktionen und darstellen.
Literatur
- Frank Olver: Asymptotics and Special Functions. Chapter 11. Academic Press, New York 1974.
- George Biddell Airy: On the intensity of light in the neighbourhood of a caustic. In: Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. Band 6, 1838, S. 379–402.
- Milton Abramowitz, Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. (siehe §10.4). National Bureau of Standards, 1954.
Weblinks
- Chapter 9: Airy and related functions. In: Digital Library of Mathematical Functions.
- Bessel-Type Functions. Wolfram Funktionenseite.
- Eric W. Weisstein: Airy Functions. In: MathWorld (englisch).
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ Eric W. Weisstein: Airy Function Zeros. In: MathWorld (englisch).
- ↑ C. Banderier, P. Flajolet, G. Schaeffer, M. Soria: Planar Maps and Airy Phenomena. In Automata, Languages and Programming. Proceedings of the 27th International Colloquium (ICALP 2000) held at the University of Geneva, Geneva, 9.–15. Juli 2000 (Ed. U. Montanari, J. D. P. Rolim, E. Welzl). Berlin: Springer, S. 388–402, 2000
- ↑ Eric W. Weisstein: Airy Zeta Function. In: MathWorld (englisch).
- ↑ Milton Abramowitz und Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 1954, Seite 447
Auf dieser Seite verwendete Medien
A surface plot of the absolute value of the Airy function:
A contour plot of the real value of the Airy function:
A contour plot of the argument of the Airy function:
A graph of the argument of the Airy Ai function over the complex plane:
A surface plot of the real part of the Airy function:
A graph of the imaginary part of the Airy Ai function over the complex plane:
A surface plot of the absolute value of the Airy function:
A surface plot of the argument of the Airy function:
Autor/Urheber: Geek3, Lizenz: CC BY 3.0
Plot of the Scorer's functions Gi(x) and Hi(x) in the interval [-10,8]:
A surface plot of the real value of the Airy function:
A surface plot of the imaginary part of the Airy function:
A surface plot of the absolute value of the Airy function:
A graph of the absolute Airy Ai function over the complex plane:
Both x and y run from -4 to 4.
A surface plot of the imaginary value of the Airy function:
A contour plot of the imaginary value of the Airy function:
A surface plot of the argument of the Airy function:




![{\displaystyle \Re \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a29ff3860d10512c63936ae57a48b1d0ba429941)

![{\displaystyle \mathrm {arg} \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1e6398901714ff29a82ca26b13f90f473377a731)

![{\displaystyle f(x)=\mathrm {arg} \left[\mathrm {Ai} x+iy\right]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c2816fb877ecf435626bbaff05e9eac05cb37f50)

![{\displaystyle f(x)=\Re \left[\mathrm {Ai} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ed7e4e3dc7e4c27038cdbddb0704de90a772bb26)

![{\displaystyle f(x)=\Im \left[\mathrm {Ai} x+iy\right]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2426b2bdbaee46abcceed59033bc1af11c299aa2)



![{\displaystyle f(x)=\mathrm {arg} \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32c132243598cd382b4cd4ca16a5591c3d22184e)




![{\displaystyle f(x)=\Re \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ebe68908b9c20d161bfcb34700bee1b632399d6f)


![{\displaystyle f(x)=\Im \left[\mathrm {Ai} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/146029b3e5c1e691b29829f65166c4d5cd74326c)







![{\displaystyle f(x)=\Im \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9bb90c5675090f2beec6e63d17cd2d9137eb329e)

![{\displaystyle \Im \left[\mathrm {Bi} (x+iy)\right]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8f90c46421a449285b47df88ca2a8b1ac3326dac)

![{\displaystyle f(x)=\mathrm {arg} \left[\mathrm {Ai} (x+iy)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6bb9145a07fc836e83059d7090044bd8d53d5710)