Antarctica Without Ice Sheet
Isostatic rebound is the result of the weight of the ice sheet depressing the land under it. After the ice is removed, the land will rise over a period of thousands of years by an amount approximately 1/3 as high as the ice sheet that was removed (because rock is 3 times as dense as ice). Approximately half the uplift occurs during the first two thousand years. If the ice sheet is removed over more than a few thousand years, then it is possible that a majority of the uplift will occur before the ice sheet fully disappears.
As indicated in the map, Antarctica consists of a large continental region (East Antarctica) and group of seas and smaller land regions (West Antarctica). Since the West Antarctic ice sheet is partially anchored below sea level, this region is less stable and more likely to be affected by global warming. Even so, it is likely that during the next century increased precipitation over Antarctica will offset melting.
Even in the event of severe sustained warming, it would take many thousands of years for Eastern Antarctica to be fully deglaciated.Relevante Bilder
Relevante Artikel
AntarktikaAntarktika ist der Südkontinent der Erde, auf dem auch der Südpol selbst liegt. Es liegt inmitten der Antarktis, mit der er umgangssprachlich oft identifiziert wird. Weitere Bezeichnungen sind Südkontinent und antarktischer Erdteil. Antarktika hat eine Fläche von etwa 14 Millionen Quadratkilometern und ist nahezu vollständig vom antarktischen Eisschild bedeckt. Geografisch unterscheidet man die Regionen Westantarktika und Ostantarktika. .. weiterlesen
KlimawandelKlimawandel, auch Klimaveränderung, Klimaänderung oder Klimawechsel, ist eine weltweit auftretende Veränderung des Klimas auf der Erde oder erdähnlichen Planeten oder Monden, die eine Atmosphäre besitzen. Die mit einem Klimawandel verbundene Abkühlung oder Erwärmung kann über unterschiedlich lange Zeiträume erfolgen. Ein wichtiges Unterscheidungsmerkmal besteht dabei zwischen jenen Witterungsverläufen, die im Rahmen eines Klimazustands beziehungsweise einer Klimazone erfolgen, und dem Klimawandel selbst, der die Wahrscheinlichkeit für das Auftreten bestimmter Wetterlagen erhöht oder vermindert. .. weiterlesen
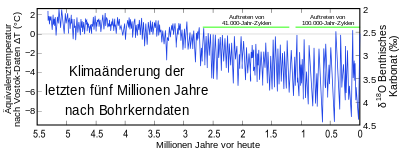
Känozoisches EiszeitalterDas Känozoische Eiszeitalter ist das gegenwärtige Eiszeitalter, das Eiszeitalter des Känozoikums (Erdneuzeit) in Abgrenzung zu den Eiszeitaltern des Paläozoikums und des Präkambriums. Sein Beginn korrespondiert mit der allmählichen Vergletscherung der Antarktis vor rund 34 Millionen Jahren. Vor etwa 2,7 Millionen Jahren setzte auch die verstärkte Eisbildung in der Arktis ein. Ab dieser Zeit wechseln sich (längere) Kaltzeiten (Glaziale) mit (kürzeren) Warmzeiten (Interglaziale) ab. .. weiterlesen